XDI’s Gross Domestic Climate Risk Index
Assam, a northeastern state of India, has been identified as one of the most vulnerable regions to climate change in the country. The Cross Dependency Initiative’s Gross Domestic Climate Risk report has ranked Assam as the 28th most vulnerable region to climate change in India. The report is based on an index that measures the physical climate risk to built environments such as buildings and properties across 2,600 states and provinces globally in 2050. The physical risk refers to vulnerability from eight climate change events: heat waves, coastal flooding (and sea level rise), extreme wind, forest fire, soil movement (or other drought-related hazards), free thaw, riverine and surface flooding.
Aggregated Damage Ratio (ADR) and its significance
According to the report, Assam, Bihar and Tamil Nadu had the highest Aggregated Damage Ratio (ADR) among other Indian states. A high ADR signifies more peril, and Assam is likely to witness the maximum increase of climate risk – rising up to 330% by 2050 as compared to 1990. This makes Assam one of the nine Indian states most vulnerable to climate change. The report’s modelling is conducted under the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s RCP 8.5 scenario – a scenario projecting high emissions, consistent with average global warming over 3 degree C above pre-industrial temperatures by the end of the century.
The report is the first physical weather risk analysis focused exclusively on the built environment and compares every state, province and territory in the world. According to XDI CEO Rohan Hamden, “Since extensive built infrastructure generally overlaps with high levels of economic activity and capital value, it is imperative that the physical risk of climate change is appropriately understood and priced.” He added, “Now – for the first time – the finance industry can directly compare Mumbai, New York and Berlin using a like-for-like methodology.”
Climate risk projection for Assam
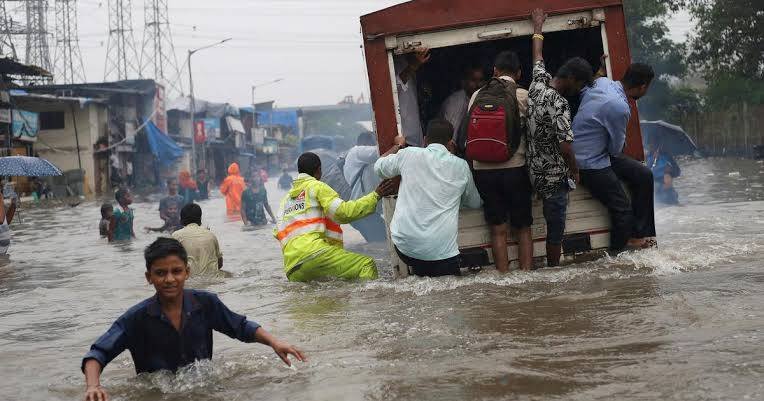
Assam has experienced an exponential increase in flood events since 2011, and it had 15 of India’s 25 districts most vulnerable to climate change, according to the State’s Science, Technology and Climate Change Minister Keshab Mahanta. Assam is prone to flooding, and riverine and surface flooding or flooding combined with coastal inundation poses the most damage to built infrastructure globally. The report pointed out that the most damage caused to built infrastructure is from “riverine and surface flooding or flooding combined with coastal inundation.”
Flood risk in Assam and Maharashtra
Assam is known for its biodiversity and is home to various species of flora and fauna. The state’s economy is heavily dependent on agriculture and forestry, and climate change poses a significant threat to the state’s agricultural production. The state is also home to the Kaziranga National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, which is known for its one-horned rhinoceroses. The park is prone to floods, and climate change is likely to increase the frequency and intensity of flooding.

The state government of Assam has taken several measures to combat the adverse effects of weather change. The state has implemented the Assam State Action Plan on Climate Change (ASAPCC) to address the challenges posed by climate change. The ASAPCC identifies six sectors – agriculture, water, forestry, health, biodiversity, and energy – and outlines strategies to mitigate the adverse impacts of climate change on these sectors. The state government has also established the Assam State Disaster Management Authority to manage and respond to disasters.
In conclusion, Assam’s vulnerability to climate change highlights the urgent need for action to mitigate its adverse effects. The state government must take proactive measures to address the challenges posed by climate change, including implementing adaptation strategies and investing in infrastructure to withstand extreme weather events. It is imperative that policymakers, civil society, and communities work together to mitigate the impacts of climate change in Assam.